枚举 贪心 暴力 前缀和
POJ1753: Flip Game 思路:
数据规模是$4 * 4$的,我们可以直接用一个char的$Map$来存储状态。
判断终点是所有的单元格的状态都相同 我们可以用一个$temp$ 然后遍历 进行判断。
注:翻转操作的时候 可能是$3$或$5$次相邻的翻转操作 我们最好是将其写成$flip$函数调用。
对$Map$从起点开始枚举每一个单元格翻转之后判断状态 类似DFS
注意回溯处理 如果反转之后要回溯一下
不翻转 即可DFS下一个单元格。详见代码
时间复杂度:
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #define IOS {ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);} #define ll long long #define SZ(X) (int)X.size() #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f using namespace std ;char Map[5 ][5 ];int ans = INF;bool check () char temp = Map[1 ][1 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i <= 4 ; i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j <= 4 ; j++) { if (Map[i][j] != temp) { return false ; } } } return true ; } void flip (int x, int y) if (Map[x][y] == 'w' ) { Map[x][y] = 'b' ; } else if (Map[x][y] == 'b' ){ Map[x][y] = 'w' ; } if (Map[x - 1 ][y] == 'w' ) { Map[x - 1 ][y] = 'b' ; } else if (Map[x - 1 ][y] == 'b' ) { Map[x - 1 ][y] = 'w' ; } if (Map[x + 1 ][y] == 'w' ) { Map[x + 1 ][y] = 'b' ; } else if (Map[x + 1 ][y] == 'b' ) { Map[x + 1 ][y] = 'w' ; } if (Map[x][y - 1 ] == 'w' ) { Map[x][y - 1 ] = 'b' ; } else if (Map[x][y - 1 ] == 'b' ) { Map[x][y - 1 ] = 'w' ; } if (Map[x][y + 1 ] == 'w' ) { Map[x][y + 1 ] = 'b' ; } else if (Map[x][y + 1 ] == 'b' ) { Map[x][y + 1 ] = 'w' ; } } void DFS (int x, int y, int cnt) if (check()) { if (cnt < ans) { ans = cnt; } return ; } if (x == 5 || y == 5 ) { return ; } flip(x, y); if (y == 4 ) { DFS(x + 1 , 1 , cnt + 1 ); } else { DFS(x, y + 1 , cnt + 1 ); } flip(x, y); if (y == 4 ) { DFS(x + 1 , 1 , cnt); } else { DFS(x, y + 1 , cnt); } } int main () IOS for (int i = 1 ; i <= 4 ; i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j <= 4 ; j++) { cin >> Map[i][j]; } } DFS(1 , 1 , 0 ); if (ans != INF) { cout << ans << endl ; } else { cout << "Impossible" << endl ; } return 0 ; }
POJ3061: Subsequence 思路:
给一个·长度为$n$的正整数序列,找出最短的子序列使其和大于等于$S$。
方法:双指针$two pointer$
我们用两个指针$i,j$来表示当前下边位置,$sum$用来表示当前的和。
因为都是正整数 所以是越加越大的 我们可以固定左指针$l$不动来移动右指针$r$,并加到$sum$直到$>=$$S$。然后我们右指针$r$可以固定不动了,以为要找最短其均为正整数。我们移动左指针$l$,即:
然后看$sum$和$S$的关系,如果满足更新$ans$,如果不满足,则继续移动右指针$r$。
复杂度:
左/右 指针最多$n$次且独立不相关 ,操作次数满足加法原理 即$2n$次
时间复杂度:
注: 双指针/尺取法 。
尺取法大概分四步:
初始化做右端点 不断扩大右端点 直到满足条件 如果第二部中条件不满足则终止,否则更新结果 将左端点扩大1,然后回到第二步
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #define IOS {ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);} #define ll long long #define SZ(X) (int)X.size() #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f using namespace std ;const int maxn = 1e5 + 5 ;int T, N, S, a[maxn];int ans;ll sum; int main () IOS cin >> T; while (T--) { cin >> N >> S; for (int i = 1 ; i <= N; i++) { cin >> a[i]; } int l = 1 , r = 1 ; sum = 0 , ans = INF; while (l <= N) { while (r <= N && sum < S) { sum += a[r]; r++; } if (sum >= S) { ans = min (ans, r - l); } sum -= a[l]; l++; } if (ans != INF) { cout << ans << endl ; } else { cout << "0" << endl ; } } return 0 ; }
NC24867: Selfish Grazing 思路:
给若干个区间,让你找这些区间内互不包含的最大区间数。
套路题:贪心策略
按照右端点进行升序排序 如果下一个区间的左端点大于上一个区间的右端点 证明不包含 $ans++$
用$now$来表示更新即可。
原因:很显然我总长度是固定的,一头牛的右端点越小给到后面牛可能吃到草的概率越大。也就是如果这个地方你不选这头牛,其他牛结束点一定比现在后,就算他起始点再好,也就和我选结束点前的方案数相同。甚至会让后面的牛选不了。
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define IOS {ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);} #define ll long long #define SZ(X) (int)X.size() #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f using namespace std ;const int maxn = 5e4 + 5 ;struct node { int l, r; }a[maxn]; bool cmp (node a, node b) if (a.r == b.r) { return a.l < b.l; } return a.r < b.r; } int N, ans, now;int main () IOS cin >> N; now = -1 ; ans = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= N; i++) { cin >> a[i].l >> a[i].r; } sort(a + 1 , a + 1 + N, cmp); for (int i = 1 ; i <= N; i++) { if (a[i].l >= now) { now = a[i].r; ans++; } } cout << ans << endl ; return 0 ; }
NC16649: 校门外的树 思路:
离散化 区间设置标记 扫一遍记录$ans$。
差分做法待补充qwq ……
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define IOS {ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);} #define ll long long #define SZ(X) (int)X.size() #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f using namespace std ;const int maxn = 1e4 + 5 ;int L, M;int l, r;int ans;int a[maxn];int main () IOS cin >> L >> M; for (int i = 0 ; i <= L; i++) { a[i] = 1 ; } for (int i = 1 ; i <= M; i++) { cin >> l >> r; for (int j = l; j <= r; j++) { a[j] = 0 ; } } for (int i = 0 ; i <= L; i++) { if (a[i] != 0 ) { ans++; } } cout << ans << endl ; return 0 ; }
NC16669:明明的随机数 思路:
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define IOS {ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);} #define ll long long #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f using namespace std ;const int maxn = 100 + 50 ;int n, x, cnt;int a[maxn];int main (void ) IOS cin >> n; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { cin >> x; if (a[x] == 0 ) { cnt++; } a[x] = 1 ; } cout << cnt << endl ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= maxn; i++) { if (a[i] != 0 ) { cout << i << " " ; } } cout << endl ; } #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define IOS {ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);} #define ll long long #define SZ(X) (int)X.size() #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f using namespace std ;int N, x;set <int >s;set <int >::iterator it;int main () IOS cin >> N; for (int i = 1 ; i <= N; i++) { cin >> x; s.insert(x); } cout << s.size () << endl ; for (it = s.begin (); it != s.end (); it++) { cout << *it << " " ; } return 0 ; }
NC20032: HNOI激光炸弹 思路:
给你一个边长为$r$的正方形,让你围成权值最大的部分。
我们可以考虑前缀和 考虑一下一维前缀和:
我们用$O(n)$的时间求出前缀和 后续查询部分和即可在$O(1)$的时间内完成。
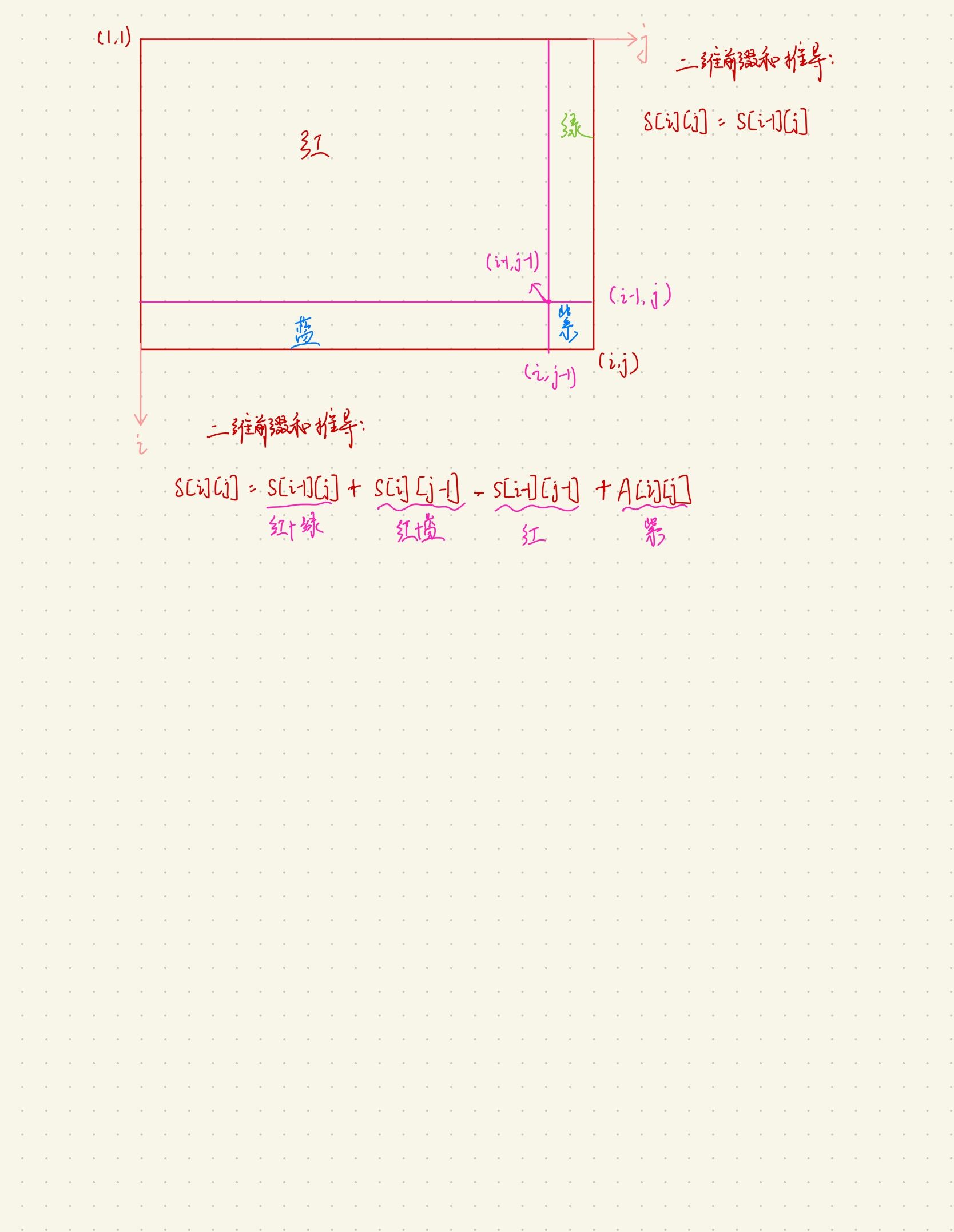
这个题涉及权值,我们可以考虑一下用二位前缀和来维护坐标为$i,j$的总权值。
二维前缀和:
如图所示:
我们可以在$O(n ^ 2)$的时间内预处理出二维前缀和$S$。
下边我们只需要找边长为$r$的区域使得权值最大
即:以$(i, j)$为右下角,边长为$r$的正方形区域的面积/权值。
细节 :
因为靠考虑前缀和 我们下标从$0$开始存储,可能会出现数组越界的错误 因此我们$x,j$都$+1$.
预处理前缀和时,可以缩小预处理的范围:
选取最小范围的正方形 这样才能保证寻找二维前缀和时初始访问位置有效
即$x = y = r$ 然后根据$x, y$选取 详见代码.
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define IOS {ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);} #define ll long long #define SZ(X) (int)X.size() #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f using namespace std ;const int maxn = 5000 + 5 ;int n, r;int ans;int sum[maxn][maxn];int main () IOS cin >> n >> r; int m_x = r, m_y = r; int x, y, w; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { cin >> x >> y >> w; x++, y++; sum[x][y] = w; m_x = max (x, m_x); m_y = max (y, m_y); } for (int i = 1 ; i <= m_x; i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j <= m_y; j++) { sum[i][j] = sum[i - 1 ][j] + sum[i][j - 1 ] - sum[i - 1 ][j - 1 ] + sum[i][j]; } } for (int i = r; i <= m_x; i++) { for (int j = r; j <= m_y; j++) { ans = max (ans, sum[i][j] - sum[i - r][j] - sum[i][j - r] + sum[i - r][j - r]); } } cout << ans << endl ; system("pause" ); return 0 ; }
NC25136:切长条 思路:
贪心策略 :
转换成求最大不相交区间数量 的问题。
我们切的时候,尽可能的使要切的区间尽可能的大。
涉及左右多因素时,可以采用结构体/pair 来处理。
因为我们找的时候 尽可能先找区间范围大的,这样在后续有可选择的余地。
上一个区间结束的越早 下一个区间就可以早开始。
于是按照区间的右端点进行升序排序,用一个变量$now$记录当前,判断下一个区间的左区间和$now$的关系。
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define IOS {ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);} #define ll long long #define SZ(X) (int)X.size() #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f using namespace std ;const int maxn = 32000 + 5 ;int N;struct node { int l, r; }a[maxn]; bool cmp (node a, node b) if (a.r == b.r) { return a.l < b.l; } return a.r < b.r; } int main () IOS cin >> N; int x; for (int i = 1 ; i <= N; i++) { cin >> a[i].l >> x; a[i].r = a[i].l + x; } sort(a + 1 , a + 1 + N, cmp); int ans = 0 ; int now = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= N; i++) { if (a[i].l >= now) { ans++; now = a[i].r; } } cout << ans << endl ; system("pause" ); return 0 ; } #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define IOS {ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);} #define ll long long #define SZ(X) (int)X.size() #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f using namespace std ;const int maxn = 32000 + 5 ;int n, len;pair<int , int > pr[maxn]; bool cmp (const pair<int , int >& a,const pair<int , int >& b) if (a.second == b.second) { return a.first < b.first; } return a.second < b.second; } int main () IOS cin >> n; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { cin >> pr[i].first >> len; pr[i].second = pr[i].first + len; } sort(pr + 1 , pr + 1 + n, cmp); int ans = 0 , now = -1 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { if (now <= pr[i].first) { ans++; now = pr[i].second; } } cout << ans << endl ; system("pause" ); return 0 ; }
NC16593:铺地毯 思路:
从后向前找 因为答案让你找最上面的,考虑一下逆向思维,后来放的肯定在前边放的上边
因此我们只需要从后往前判断有没有符合的区间包含这个点即可。二维平面 两个$if$判断一下。
然后如果有的话 输出然后$return 0;$即可,因为只让输出最上边的。
【同样可以打一个$flag$标记,然后判一下】
注意:!!!
该题空间给的是128MB,我们计算一下如果开二维数组,可能会有爆空间的风险……
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define IOS {ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);} #define ll long long #define SZ(X) (int)X.size() #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f using namespace std ;const int maxn = 1e4 + 5 ;int n;int a[maxn], b[maxn], g[maxn], k[maxn];int x, y;int main () IOS cin >> n; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { cin >> a[i] >> b[i] >> g[i] >> k[i]; } cin >> x >> y; for (int i = n; i > 0 ; i--) { if (x >= a[i] && x <= a[i] + g[i]) { if (y >= b[i] && y <= b[i] + k[i]) { cout << i << endl ; return 0 ; } } } cout << "-1" << endl ; system("pause" ); return 0 ; }
NC16640:纪念品分组 思路:
类似POJ3061:Subsequence的思路,采用双指针来解决。
排序 然后两个指针扫一遍 如果满足的话 都移动然后$ans++$,不满足的话,右指针左移值减小,然后右边的单独放一个。
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define IOS {ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);} #define ll long long #define SZ(X) (int)X.size() #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f using namespace std ;const int maxn = 30000 + 5 ;int a[maxn];int w, n;int ans;int main () IOS cin >> w >> n; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { cin >> a[i]; } sort(a + 1 , a + 1 + n); int l = 1 , r = n; while (l <= r) { if (a[l] + a[r] <= w) { ans++, l++,r--; } else { ans++; r--; } } cout << ans << endl ; system("pause" ); return 0 ; }
NC16783:拼数 思路:
因为是拼接操作,我们可以把数字当成字符串来处理,考虑拼接我们可以将每一个字符串排序,按照拼接后的顺序写$cmp$函数
这一步非常巧妙,假设$a=321,b=32$,$a+b=32132,b+a=32321$这样下面sort排下来就是32>321避免出现32132>32321的情况 ,因此我们采用拼接再排序。
然后按照升序排列后从后往前输出即可。
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define IOS {ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);} #define ll long long #define SZ(X) (int)X.size() #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f using namespace std ;const int maxn = 20 + 5 ;int n;string s[maxn];bool cmp (string a, string b) return a + b < b + a; } int main () IOS cin >> n; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { cin >> s[i]; } sort(s + 1 , s + 1 + n, cmp); for (int i = n; i >= 1 ; i--) { cout << s[i]; } cout << endl ; system("pause" ); return 0 ; }
NC15553:数学考试 思路1:
求两段连续不相交的子区间使和最大。
考虑先用前缀和维护出某一段的区间和。
然后我们要求某个位置之前和之后的和最大 的区间。
线性DP求一下 设$l_i$表示位置$i$之前的最大区间和,$r_i$表示位置$i$之后的最大区间和。
因此有:
注意数据范围还有遍历范围 详见代码……
注意点:
$ans$的取值要取尽可能小…不然只过83.3%的数据范围…【其实我也不知道开多大qwq】
这题玄学…memset能过 遍历赋值过不了qwq
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define IOS {ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);} #define ll long long #define SZ(X) (int)X.size() #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f using namespace std ; const int maxn = 2e5 + 5 ;int T, n, k;int a[maxn];ll sum[maxn]; ll l[maxn], r[maxn]; ll ans; int main () IOS cin >> T; while (T--) { cin >> n >> k; ans = -1e18 ; memset (l, -INF, sizeof (l)); memset (r, -INF, sizeof (r)); for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { cin >> a[i]; sum[i] = sum[i - 1 ] + a[i]; } for (int i = k; i <= n - k; i++) { l[i] = max (l[i - 1 ], sum[i] - sum[i - k]); } for (int i = n - k + 1 ; i >= k + 1 ; i--) { r[i] = max (r[i + 1 ], sum[i + k - 1 ] - sum[i - 1 ]); } for (int i = k; i <= n - k; i++) { ans = max (ans, l[i] + r[i + 1 ]); } cout << ans << endl ; } system("pause" ); return 0 ; }
思路2:
前缀和处理之后,维护前缀和中长度为k的最大值m1,枚举第二个长度为k的起点,答案就是max(m1 + 当前长度为k的序列和).
时间复杂度:$O(n)$
注意枚举的范围 $i + k <= n$,要留出第二个的范围。
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define IOS {ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);} #define ll long long #define SZ(X) (int)X.size() #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f using namespace std ;const int maxn = 2e5 + 5 ;int T, n, k;int a[maxn];ll sum[maxn]; int main () IOS cin >> T; while (T--) { for (int i = 1 ; i <= maxn; i++) { a[i] = sum[i] = 0 ; } cin >> n >> k; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { cin >> a[i]; sum[i] = sum[i - 1 ] + a[i]; } ll m1 = -1e18 , ans = -1e18 ; for (int i = k; i + k <= n; i++) { m1 = max (m1, sum[i] - sum[i - k]); ans = max (ans, m1 + sum[i + k] - sum[i]); } cout << ans << endl ; } system("pause" ); return 0 ; }
NC16561:国王的游戏 思路:
贪心思路+高精度【涉及大数乘除运算】…
贪心证明见PPT, 高精度还是用$Python$写舒服啊[滑稽~]
贪心数学证明可见:https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/solution/P1080
pthyon写法详见:https://www.cnblogs.com/coderzjz/p/12745550.html
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 n = int(input()) s = input().split() S = int(s[0 ]) a = [] for i in range(1 , n + 1 ): k = input().split() a.append((int(k[0 ]), int(k[1 ]))) a.sort(key=lambda x: x[0 ] * x[1 ]) ans = 0 for i in range(0 , n): if (S // (a[i])[1 ] > ans): ans = S // (a[i])[1 ] S *= (a[i])[0 ] print(ans)
NC24636:值周 思路:
类似题目NC16649:校门外的树
题目范围$L$和$M$过大,如果嵌套的话,必定超时 我们考虑每次操作修改的实际是大区间中的小区间值,于是我们可以考虑离散化 处理。
我们按照区间的左端点进行升序排序,然后处理。
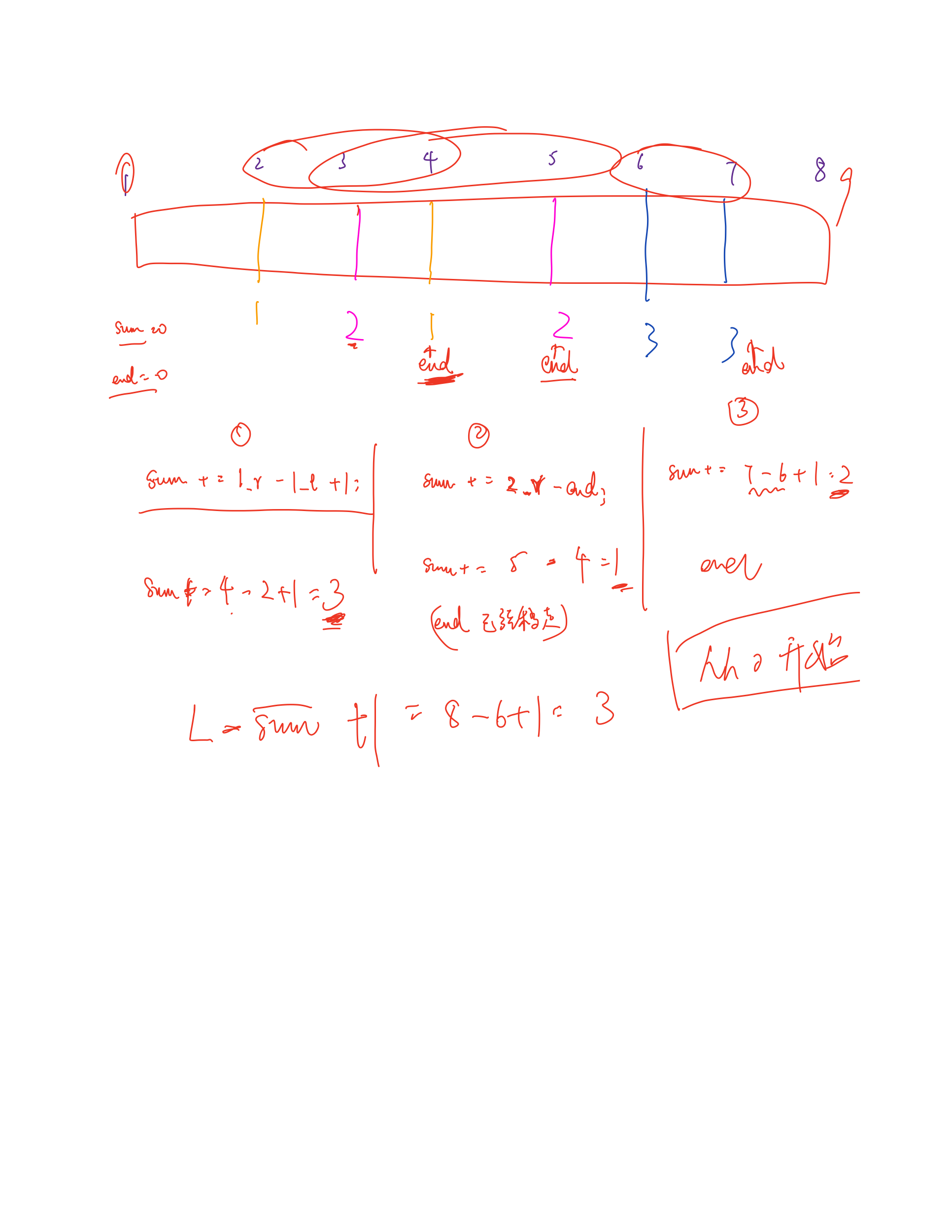
画个图可以理解一下区间的覆盖
第一个区间被移走的人数是$r-l+1$,标记当前$end=r$。
如果下一个区间的$l$比$end$大,移走的人数是$r-l+1$,更新$end$。
如果下一个区间的$r$不小于$end$,移走的人数是$r-end$,更新$end$。
最后剩余的是$L - sum + 1$。输出的时候,注意位置 0 也有一棵树,所以总数量要加 1 。
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define IOS {ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);} #define ll long long #define SZ(X) (int)X.size() #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f using namespace std ;const int maxn = 1e6 + 5 ;ll L, M; ll l, r; pair<ll, ll>pr[maxn]; int main () IOS cin >> L >> M; for (int i = 1 ; i <= M; i++) { cin >> l >> r; pr[i] = make_pair(l, r); } sort(pr + 1 , pr + 1 + M); ll sum = 0 , end = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= M; i++) { if (pr[i].first >= end ) { sum += pr[i].second - pr[i].first + 1 ; end = pr[i].second; } else if (pr[i].second >= end ) { sum += pr[i].second - end ; end = pr[i].second; } } cout << L - sum + 1 << endl ; return 0 ; }
还有一种是差分思路。可以尝试理解一下,记录区间端点的变化,而不关心区间内部的细节。
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define IOS {ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);} #define ll long long #define SZ(X) (int)X.size() #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f using namespace std ;const int maxn = 1e8 + 5 ;int a[maxn];int L, M;int l, r;int main () IOS cin >> L >> M; a[0 ] = 1 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= M; i++) { cin >> l >> r; a[l] += 1 ; a[r + 1 ] -= 1 ; } ll sum = 0 , ans = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i <= L; i++) { sum += a[i]; if (sum == 1 ) { ans++; } } cout << ans << endl ; return 0 ; }
NC14709:奇♂妙拆分 思路:
枚举思路
考虑类似质因数分解,但要求分解的不可以有重复的,例如分解$7$,可以分解成$1$和$7$的组合。其中一部分肯定大于$sqrt(n)$。所以我们可以设置$ans$的初始值为$1$,表示总有一个数字大于$sqrt(n)$的因子。
这样我们下边就可以模仿分解质因数的方式,满足不重复即可,把$while$条件改成$if$,如果满足就分解出该因子即可,按照从小到大的顺序。
可能在一遍循环之后,n并没有如愿的变成1(有些情况下因数大于$sqrt(n)$,有些情况下i大于当前的n且n没能变为1),所以我们要分别考虑这两种情况,对第一种情况,这种因数只会出现一次,所以在循环结束后将$res + 1$即可,对于第二种情况,这个n一定不能作为新的质因数产生了,因为如果它是一个新的质因数,那么i在循环到该值时会产生对应的质因数,所以它只能与其他数一起产生一个合数。
代码:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define IOS {ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);} #define ll long long #define SZ(X) (int)X.size() #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f using namespace std ;int T, n;void solve () int ans = 1 ; for (int i = 1 ; i * i < n; i++) { if (n % i == 0 ) { ans++; n /= i; } } cout << ans << endl ; } int main () IOS cin >> T; while (T--) { cin >> n; solve(); } system("pause" ); return 0 ; }
NC14583:糖糖别胡说,我真的不是签到题目 思路:
考虑糖糖消失有条件:
实际上,糖糖的消失并没有直接的关系,发功影响的是整个区间的值都$+1$。
区间都增加/减少问题我们可以考虑差分数组来维护再求前缀和来降低复杂度。就是每次记录区间的更改,然后再更新整个区间emm
注意每次干掉都是干掉之前的小的,如果从前往后判断,每次都要找比当前小的值,因此,我们题意可以维护最大值,从后向前维护两组的各自最大值,并保留.
emm…看代码就可以辣~
注意可以用结构体来存,空间开大点…
代码:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define IOS {ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);} #define ll long long #define SZ(X) (int)X.size() #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f using namespace std ; const int maxn = 5e6 + 5 ;struct node { int id; int value; }sweet[maxn]; int T;int n, m;int c[maxn], d[maxn];int main () IOS cin >> T; while (T--) { memset (d, 0 , sizeof (d)); cin >> n >> m; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { cin >> sweet[i].id >> sweet[i].value; } for (int i = 1 ; i <= m; i++) { cin >> c[i]; d[1 ]++; d[c[i] + 1 ]--; } ll sum = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { sum += d[i]; sweet[i].value += sum; } ll max1 = -INF, max2 = -INF; ll ans = 0 ; for (int i = n; i > 0 ; i--) { if (sweet[i].id) { max1 = max (max1, (ll)sweet[i].value); if (sweet[i].value >= max2) { ans++; } } else { max2 = max (max2, (ll)sweet[i].value); if (sweet[i].value >= max1) { ans++; } } } cout << ans << endl ; } system("pause" ); return 0 ; }
NC53681:「土」巨石滚滚 思路:
典型贪心。
我们很容易凭借感觉可以确定我们每次选择的时候都是优先选择增加稳定性值大的。
当我们都是增加稳定性时,优先选择消耗值小的,这样可以避免后边出现很大的时,稳定值不足。
当都是减少稳定性时,优先选择反馈值大的,这样可以消耗少一点。
qwq想一下就可以了 具体的排序$cmp$实现可以参考代码(qwq其实我也不长写这种 逻辑要写对……)
贪心排序之后,用一个$flag$标记一下即可 终止条件就是下一个消耗的比当前存储的大,即证明不可以继续贪心即可。
代码:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define IOS {ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);} #define ll long long #define SZ(X) (int)X.size() #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f using namespace std ;const int maxn = 5e5 + 5 ;struct node { int x, y, val; bool operator < (const node& a) const { if (val > 0 && a.val > 0 ) { return x < a.x; } if (val < 0 && a.val < 0 ) { return y > a.y; } return val > a.val; } }stone[maxn]; int T, n, m;int main () IOS cin >> T; while (T--) { cin >> n >> m; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { cin >> stone[i].x >> stone[i].y; stone[i].val = stone[i].y - stone[i].x; } sort(stone + 1 , stone + 1 + n); ll sum = m; bool flag = true ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { if (stone[i].x > sum) { flag = false ; break ; } sum += stone[i].val; } if (flag) { cout << "Yes" << endl ; } else { cout << "No" << endl ; } } system("pause" ); return 0 ; }
NC200190:矩阵消除游戏 思路:
贪心策略……
连接:
https://blog.nowcoder.net/n/6bcd181f88684b9a85c359f84a44539e
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define IOS {ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);} #define ll long long #define SZ(X) (int)X.size() #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f using namespace std ;const int maxn = 15 + 5 ;int n, m, k; int matrix[maxn][maxn];ll rowsum[maxn], columnsum[maxn]; bool bit [maxn];ll ans; int convert (int x) memset (bit , 0 , sizeof (bit )); int cnt = 0 , i = 1 ; while (x) { if (x & 1 ) { bit [i] = 1 ; cnt++; } x >>= 1 ; i++; } return cnt; } int main () IOS cin >> n >> m >> k; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j <= m; j++) { cin >> matrix[i][j]; rowsum[i] += matrix[i][j]; } } if (k > n) { k = n; } if (k > m) { k = m; } int tmp = (1 << n) - 1 ; for (int T = 0 ; T <= tmp; T++) { int numrow = convert(T); int numcolumn = k - numrow; if (numrow > n || numcolumn > m || numrow < 0 || numcolumn < 0 ) { continue ; } ll sum = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { if (bit [i]) { sum += rowsum[i]; } } memset (columnsum, 0 , sizeof (columnsum)); for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j <= m; j++) { if (!bit [i]) { columnsum[j] += matrix[i][j]; } } } sort(columnsum + 1 , columnsum + 1 + m); for (int i = 1 , j = m; i <= numcolumn; i++, j--) { sum += columnsum[j]; } ans = max (ans, sum); } cout << ans << endl ; system("pause" ); return 0 ; }
!!!第一次的题解终于写完啦~
!!!耗时2周qwq~
!!!太菜辽~